The registered runner uses the ruby:2.6 Docker image and runs two services, postgres:latest and mysql:latest, both of which are accessible during the build process. What is an image. The image keyword is the name of the Docker image the Docker executor runs to perform the CI tasks. By default, the executor pulls images only from Docker Hub. Note: To run the docker command without sudo, create the docker group and add your user. For details, see the post-installation steps for Linux. Download a TensorFlow Docker image. The official TensorFlow Docker images are located in the tensorflow/tensorflow Docker Hub repository. Image releases are tagged using the following format.
Last week, during the Docker Community All Hands, we announced the availability of a developer preview build of Docker Desktop for Macs running on M1 through the Docker Developer Preview Program. We already have more than 1,000 people testing these builds as of today. If you’re interested in joining the program for future releases you should do it today!
As I’m sure you know by now, Apple has recently shipped the first Macs based on the new Apple M1 chips. Last month my colleague Ben shared our roadmap for building a Docker Desktop that runs on this new hardware. And I’m delighted to tell you that today we have a public preview that you can download and try out.
Bluestacks download on mac. Like many of you, we at Docker have been super excited to receive and code with these new computers: they just feel so fast! We also know that Docker Desktop is a key part of the development cycle for over 3M developers using Docker Desktop with over half of you on Macs. To support all our Mac users we’ve been working hard to get Docker Desktop ready to run on the new M1 hardware. It is not release quality yet, or even beta quality, but we have an early preview build and we wanted to let you try it as soon as possible.
Download el capitan iso. How We Got to a Technical Preview
When Ben announced that we were working on adapting Docker Desktop on this new hardware. We had roughly 3 engineering challenges to tackle to get this release out to you:
- Migrate from HyperKit to the Virtualization Framework.
One of the key challenges for the Docker Desktop team was to replace HyperKit, which Docker open sourced back in 2016, with the Virtualization Framework provided by Apple which was included in macOS Big Sur.
- Recompile all the various binaries of Docker Desktop in native arm.
Many of the tools that we use in our toolchain to build these binaries are not yet ready to support the M1 Mac as of today. At Docker, we use the Go language extensively, and Docker Desktop is no exception. The Go language will support Apple Silicon in their 1.16 release which is targeted for February 2021.
- Have enough hardware to reliably run continuous deployment on M1 macs.
The Docker Desktop team relies heavily on automated testing through continuous integration to ensure the quality of our releases. Until this week our continuous integration could not be set up because none of our partners had enough M1 machines yet. Fortunately, we are working with MacStadium and we are setting up new M1 Macs on our CI system.
Thanks to the significant progress we have been able to make on the first two steps, we are sharing a Tech Preview of Docker Desktop for M1 today. Download it here!
Multi-Platform Baked In
Many developers are going to experience multi-platform development for the first time with the M1 Macs. This is one of the key areas where Docker shines. Docker has had support for multi-platform images for a long time, meaning that you can build and run both x86 and ARM images on Desktop today. The new Docker Desktop on M1 is no exception; you can build and run images for both x86 and Arm architectures without having to set up a complex cross-compilation development environment.
Docker Hub also makes it easy to identify and share repositories that provide multi-platform images.
And finally, using docker buildx you can also easily integrate multi-platform builds into your build pipeline.
Try the M1 Preview Today
Right on time for the year-end festivities, we’re excited to share with you our M1 Preview:

Here is the Download!
Keep in mind that this is a preview release: it may break, it has not been tested as thoroughly as our normal releases and ‘here be dragons’. Your help is needed to test Docker Desktop on Apple Silicon so that we can continue to provide a great developer experience on all Apple devices. You can help us by providing bug reports on docker/for-mac. We will use this feedback to help us improve and iterate on both the Desktop product and the multi-architecture experience as we aim to provide a GA build of Docker Desktop in the first quarter of 2021.
Docker Download Image And Running
In the meantime, enjoy this tech preview build of Docker Desktop for M1. Happy Holidays!
Docker uses containers tocreate virtual environments that isolate a TensorFlow installation from the restof the system. TensorFlow programs are run within this virtual environment thatcan share resources with its host machine (access directories, use the GPU,connect to the Internet, etc.). TheTensorFlow Docker images are tested for each release.
Docker is the easiest way to enable TensorFlow GPU support on Linux since only theNVIDIA® GPU driver is required on the host machine (the NVIDIA® CUDA® Toolkit does not need tobe installed).
TensorFlow Docker requirements
- Install Docker onyour local host machine.
- For GPU support on Linux, install NVIDIA Docker support.
- Take note of your Docker version with
docker -v. Versions earlier than 19.03 require nvidia-docker2 and the--runtime=nvidiaflag. On versions including and after 19.03, you will use thenvidia-container-toolkitpackage and the--gpus allflag. Both options are documented on the page linked above.
- Take note of your Docker version with
docker command without sudo, create the docker group andadd your user. For details, see thepost-installation steps for Linux.Download a TensorFlow Docker image
The official TensorFlow Docker images are located in the tensorflow/tensorflow Docker Hub repository. Image releases are tagged using the following format:
| Tag | Description |
|---|---|
latest | The latest release of TensorFlow CPU binary image. Default. |
nightly | Nightly builds of the TensorFlow image. (Unstable.) |
version | Specify the version of the TensorFlow binary image, for example: 2.1.0 |
devel | Nightly builds of a TensorFlow master development environment. Includes TensorFlow source code. |
custom-op | Special experimental image for developing TF custom ops. More info here. |
Each base tag has variants that add or change functionality:
| Tag Variants | Description |
|---|---|
tag-gpu | The specified tag release with GPU support. (See below) |
tag-jupyter | The specified tag release with Jupyter (includes TensorFlow tutorial notebooks) |
You can use multiple variants at once. For example, the following downloadsTensorFlow release images to your machine:
Start a TensorFlow Docker container
To start a TensorFlow-configured container, use the following command form:
For details, see the docker run reference.
Examples using CPU-only images
Let's verify the TensorFlow installation using the latest tagged image. Dockerdownloads a new TensorFlow image the first time it is run:
Let's demonstrate some more TensorFlow Docker recipes. Start a bash shellsession within a TensorFlow-configured container:
Within the container, you can start a python session and import TensorFlow.
To run a TensorFlow program developed on the host machine within a container,mount the host directory and change the container's working directory(-v hostDir:containerDir -w workDir):
Permission issues can arise when files created within a container are exposed tothe host. It's usually best to edit files on the host system.
Start a Jupyter Notebook server usingTensorFlow's nightly build:
Follow the instructions and open the URL in your host web browser:http://127.0.0.1:8888/?token=..
GPU support
Docker is the easiest way to run TensorFlow on a GPU since the host machineonly requires the NVIDIA® driver (the NVIDIA® CUDA® Toolkit is not required).
Install the Nvidia Container Toolkit to add NVIDIA® GPU support to Docker. nvidia-container-runtime is onlyavailable for Linux. See the nvidia-container-runtimeplatform support FAQ for details.
Check if a GPU is available:

Verify your nvidia-docker installation:
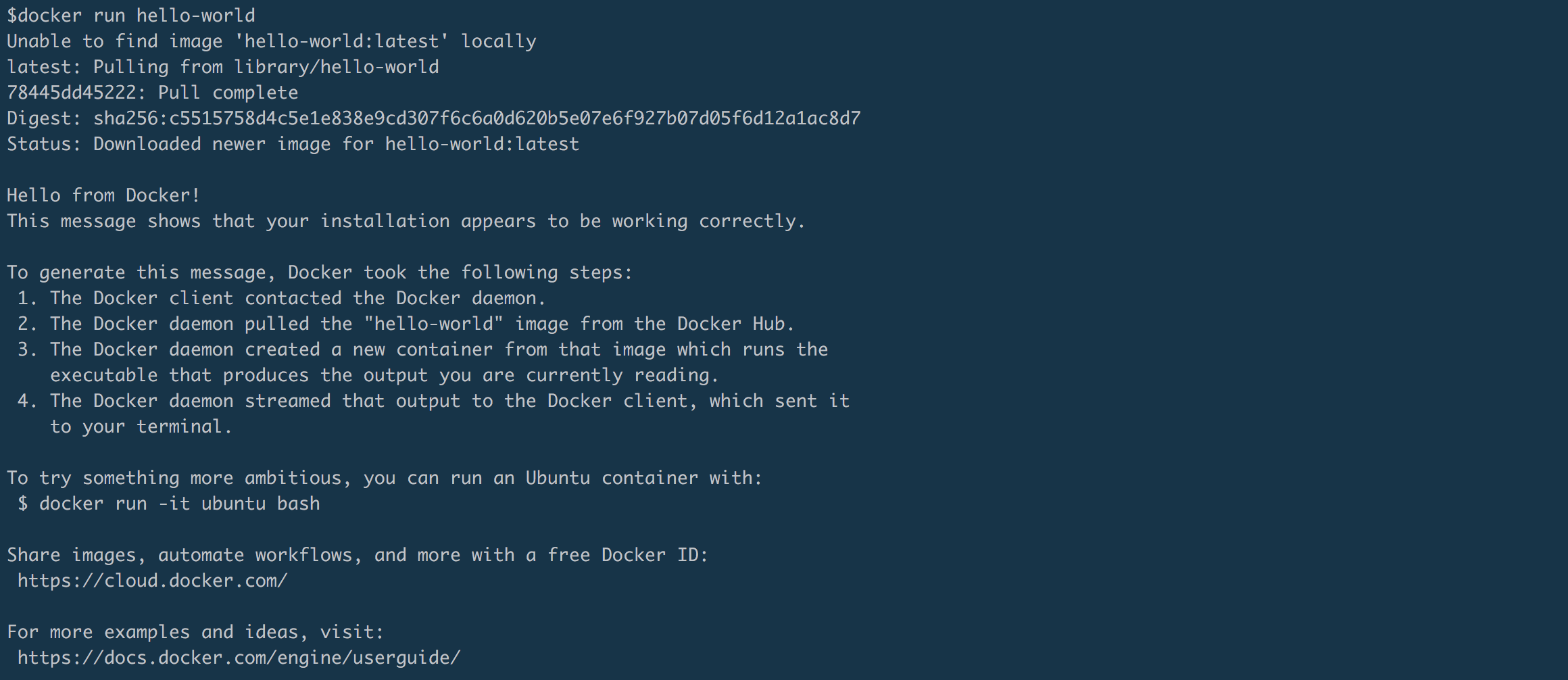
nvidia-docker v2 uses --runtime=nvidia instead of --gpus all. nvidia-docker v1 uses the nvidia-docker alias, rather than the --runtime=nvidia or --gpus all command line flags.Examples using GPU-enabled images
Download and run a GPU-enabled TensorFlow image (may take a few minutes):
It can take a while to set up the GPU-enabled image. If repeatedly runningGPU-based scripts, you can use docker exec to reuse a container.
Docker Download Image And Runner
Use the latest TensorFlow GPU image to start a bash shell session in the container:
Docker Download Image Manually
TensorFlow is now installed. Read the tutorials to getstarted.